STRUCTURES

CULTURAL HERITAGE PROTECTION THROUGH ADVANCED NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS
The Armenian government commissioned the National University of Architecture and Construction of Armenia to coordinate a group of Italian and Armenian experts for the preservation of the basilica of Ererouyk. Politecnico di Milano was involved in the work, performing the vulnerability analysis of the Basilica and the design of the strengthening, as described in this document.

STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING OF EXISTING DAMS
The research explores the use and performance of Machine Learning tools to interpret the large amount of data collected by the monitoring systems installed in existing dams.
The work is carried out in collaboration with the Italian Commission on Large Dams (ITCOLD) and the company RSE.
This activity also aims at providing quality education to a new generation of dam experts.
ENERGY PRODUCTION INFRASTRUCTURES
DICA is committed to advancing the sustainability of energy production infrastructure. With the global transition from carbon-based fuels to renewable energy sources, there has been a notable increase in onshore wind turbine towers installation. One avenue to boost both their sustainability and competitiveness lies in the optimization of their reinforced concrete shallow foundations. Experimental and numerical studies conducted at Polimi have recently investigated the effects of varied reinforcement layouts on these foundations under extreme wind conditions.
EVERYDAY CHALLENGE OF SEISMIC RISK
The Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering is internationally acknowledged for its scientific contributions to the research for seismic risk protection, with relevant collaborations with public institutions (Department of Civil Protection, European Commission) and industry (swissnuclear, EDF, Munich RE). Such research allows for investing on the future of our societies, enhancing the safety and resilience of built environments against potential adverse events.
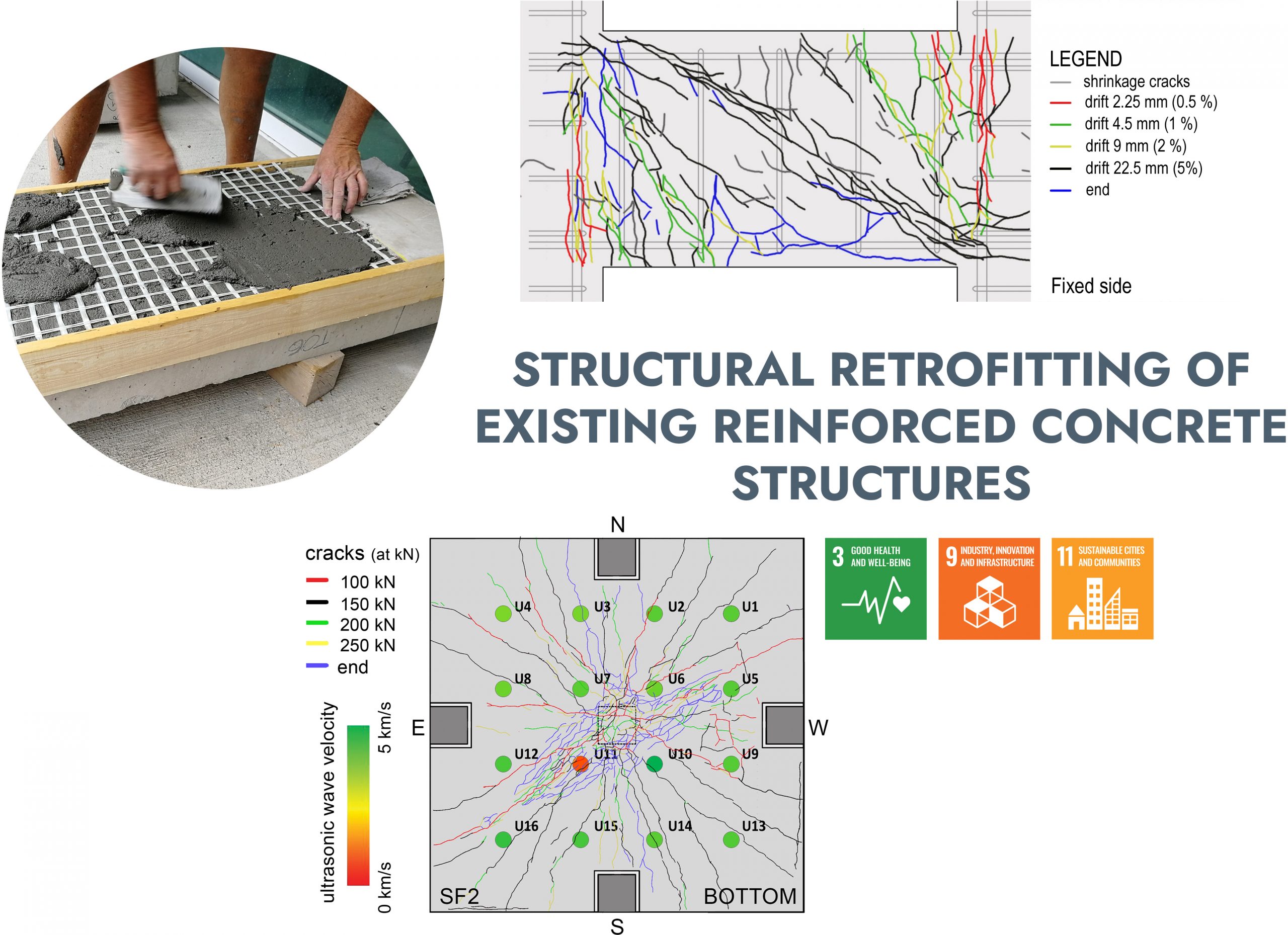
STRUCTURAL RETROFITTING OF EXISTING REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES
The structural performance and long-term durability of existing reinforced concrete structures can be substantially compromised by deterioration and environmental factors. This research concentrated on introducing innovative retrofitting methods that can prolong the operational lifespan of structural components such as under-reinforced shallow beams, plates, and coupling beams. Various fabric-reinforced cementitious matrix (FRCM) solutions were applied on full-scale elements previously subjected to damage and surface machining. The approach allowed the examination of the retrofitting solutions efficacy under static and oligo-cyclic loads, further promoting the widespread adoption of these composites in real retrofitting applications.
Prof. Marco di Prisco, Prof. Matteo Colombo, PhD Giulio Zani, PhD Marco Carlo Rampini
NOVEL TRANSPORTATION INFRASTRUCTURES
Submerged FloatingTunnels are watertight tunnels located underwater and kept in place by pontoons or mooring systems. Although a realization of SFTs is still to be accomplished, they are recognized as a promising alternative to long-span bridges and immersed tunnels for crossing waterways.
Since most of the structure is located under the water table, SFTs have the advantage of a very small, or virtually zero, visual impact on the landscape and a small occupation of soil. Moreover, SFTs are less prone than other crossing solutions to interruptions or limitations of the operability due to harsh weather conditions.
Research at DICA deals with the modeling of the dynamic response of SFTs under traffic-induced and environmental loads (earthquakes, current, waves).
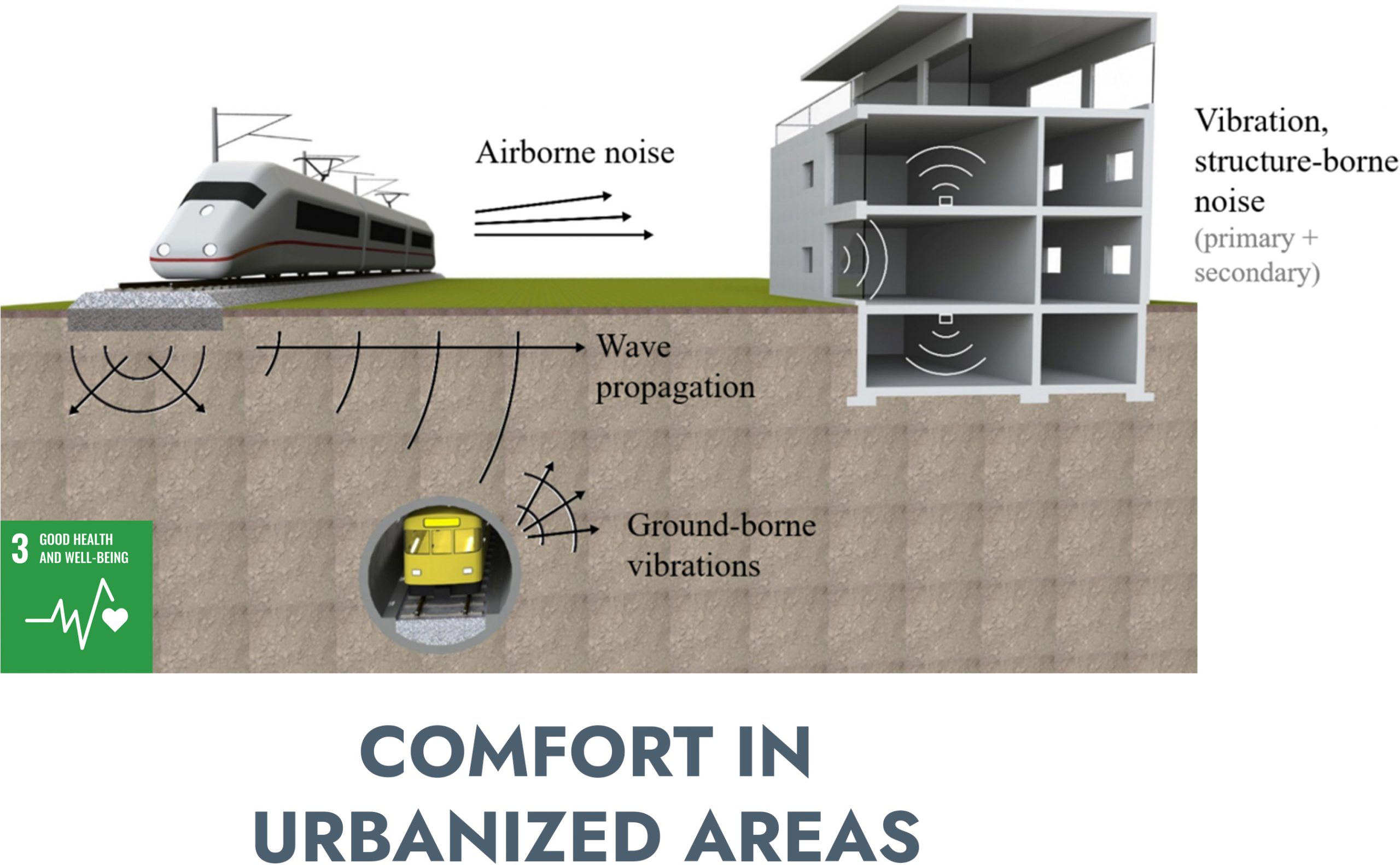
The passage of underground trains produces both noise and vibrations which, in urban settings, can affect the comfort of people occupying the buildings nearby the railway route.
Besides by the train-track properties, the excitation produced by trains is affected also by the geometry and material of the tunnel as well as the properties of the surrounding soils.
Change in train operational weight or speed, together with the natural ageing of the railway track infrastructure, or change is the soil properties, can cause a variation of the vibration level over time, leading to potentially annoying situations.
DICA has been involved in assessing the effect of some of this changes as described in this document.
Dynamic testing, a non-destructive experimental technique widely employed to assess serviceability (e.g. comfort) conditions of structures, is at the base of procedures to identify important structural parameters.
Based on measurements of structural vibration, dynamic testing can be performed in operational conditions without interrupting the normal usage of the structure.
Monitoring time variations of the identified structural properties is of paramount importance for safety assessment and early damage detection, and is at the base of Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) approaches.
Research at DICA is active both in field of assessment of the structure serviceability (see this link) and of SHM (see this link).
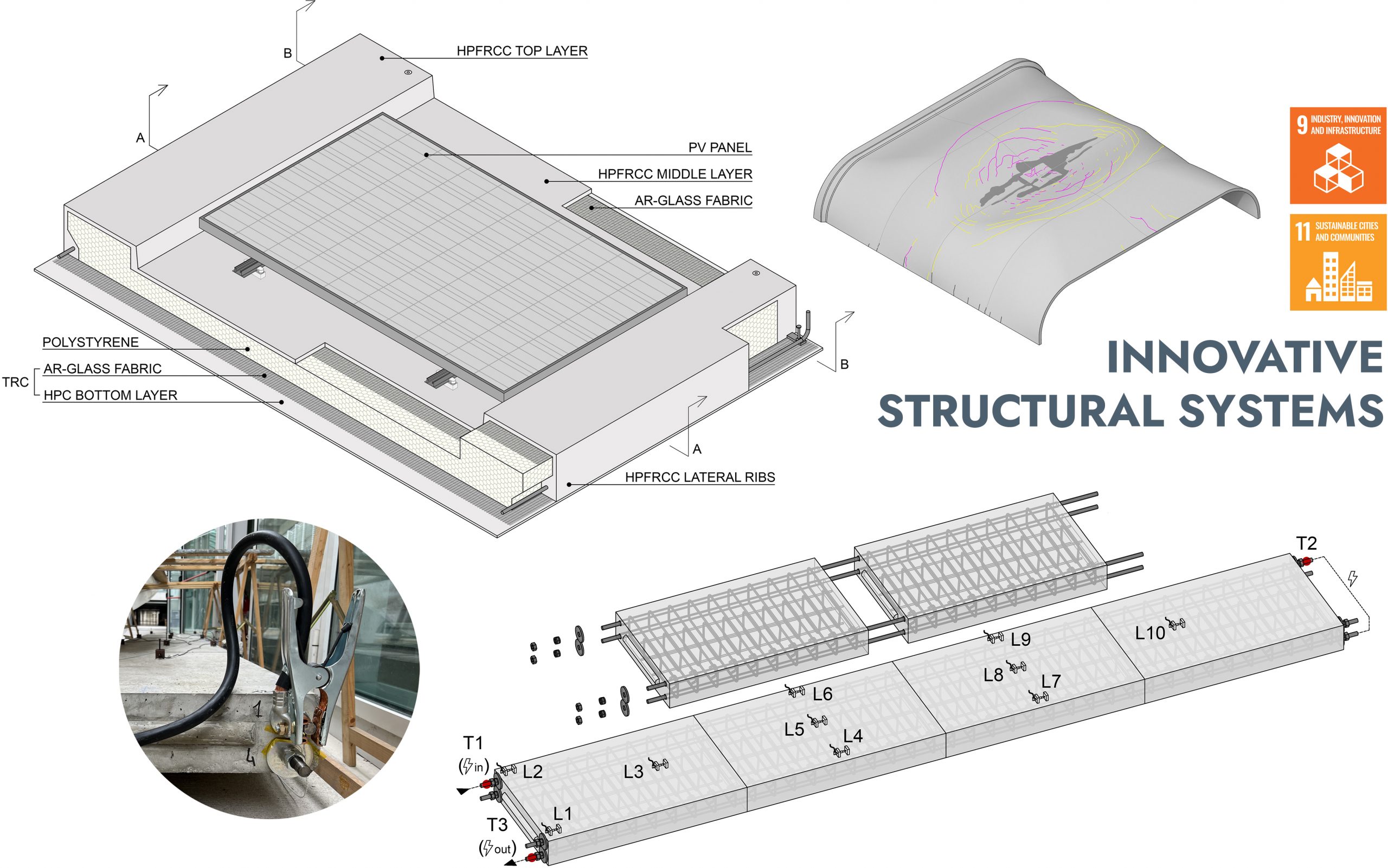
INNOVATIVE CEMENT-BASED STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS
Innovative cement-based structures made of high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete (HPFRC), textile-reinforced concrete (TRC), or using recycled materials along with memory-steel post-tensioning techniques showcase a new era in contemporary construction. These structures not only bolster structural integrity but also align with sustainability goals. The development of innovative structures, undertaken at DICA in close partnership with scientific and industrial collaborators, allowed the examination of structural performance through full-scale specimens and the validation of simplified design approaches and advanced nonlinear models. In addition, it entailed evaluating the significant hurdles encountered in transferring state-of-the-art construction technologies developed in the laboratory to practical prefabrication facilities.
Prof. Marco di Prisco, Prof. Matteo Colombo, PhD Giulio Zani, PhD Marco Carlo Rampini
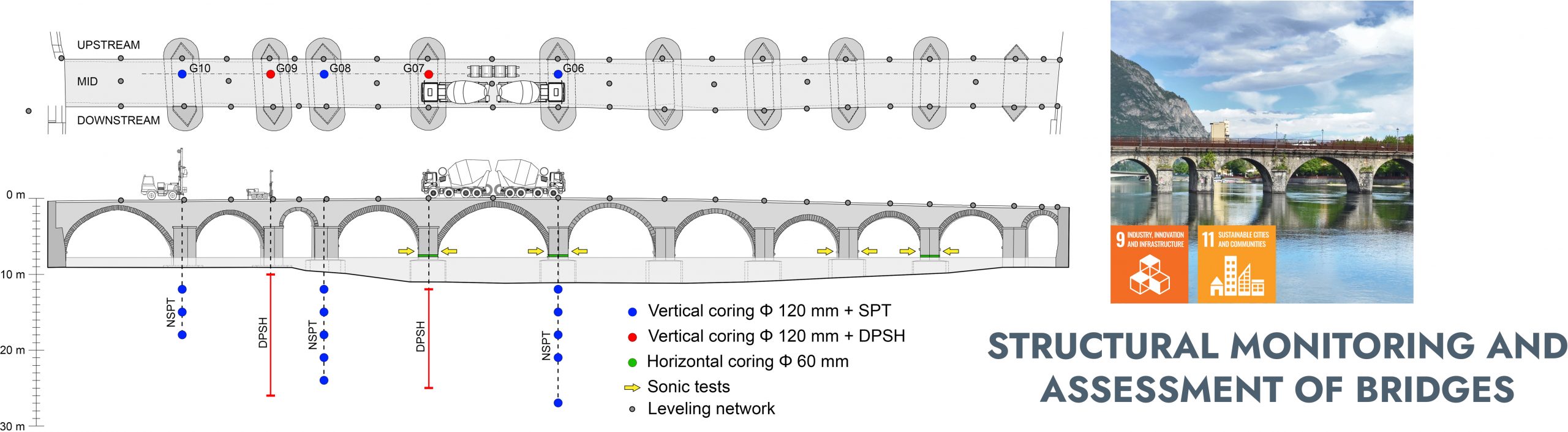
STRUCTURAL MONITORING AND ASSESSMENT OF BRIDGES
STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT OF THE AZZONE VISCONTI BRIDGE IN LECCO
The conservation and the structural safety of historical structures belonging to a country’s cultural heritage are two main concerns in our society. Historical bridges are valuable structures exposed to potential damage due to different causes: increase in vehicular traffic, increase in maximum allowable accidental loads, effects of pollution, presence of vegetation, action of water currents and occurrence of natural hazards, such as floods and earthquakes. In collaboration with the Municipality of Lecco, this research investigated the bearing capacity and seismic vulnerability of the Azzone Visconti Bridge, a historic stone arch bridge dating back to the 14th century. The study employed both experimental and numerical methodologies, also considering the intricate interplay between the structure and its foundation in response to gravitational and seismic forces.
Prof. Marco di Prisco, Prof. Matteo Colombo, Prof. Andrea Galli, Prof. Paolo Martinelli, PhD Giulio Zani
IN-SCALE STRUCTURES SUBJECTED TO IMPACT, BLAST AND FIRE
In-scale tests on structural elements subjected to accidental actions are performed at a lab that is equipped with a Shock Tube that is unique in the world for its application, dimension and performance (1). The maximum design reflected pressure generated by the equipment is equal to 3 MPa and the maximum shock wave velocity is equal to 3 Mach. The main innovative point of this instrument is its capability to investigate the soil-structure interaction (2) and, by means a movable furnace, also the blast/fire interaction (3) on scaled structures.